Navigating Hyperprolactinemia: From Irregular Periods and Infertility to Pituitary Tumours

Introduction
Think about the woman who does not understand why her menstruation is not regular and why she has unexpected milk, or a couple who have problems with unexpected infertility. Quite commonly, it has its root in hyperprolactinemia or increased prolactin hormone. This guide leads you through its typical symptoms, starting with disruptive cycles and progressing to poor libido. We will examine its varied causes, such as medications and pituitary tumours, and outline the definitive diagnostic and treatment options that one can choose. Learning to live with this condition is the initial step to successful management, and you will be able to pursue the appropriate care and restore your health.
What is Prolactin and Why Does It Matter?
Prolactin refers to a hormone that majorly induces the production of breast milk (lactation) following delivery. Nevertheless, levels may rise even out of the state of pregnancy or breastfeeding, which is usually a red flag of some underlying health concern. This is known as hyperprolactinemia and may interfere with ovulation, leading to infertility, irregular periods, and spontaneous milk discharge. This is important as it is often caused by a harmless pituitary tumour, some drugs, or thyroid issues. The root cause of these symptoms must be detected and treated to restore hormonal balance.
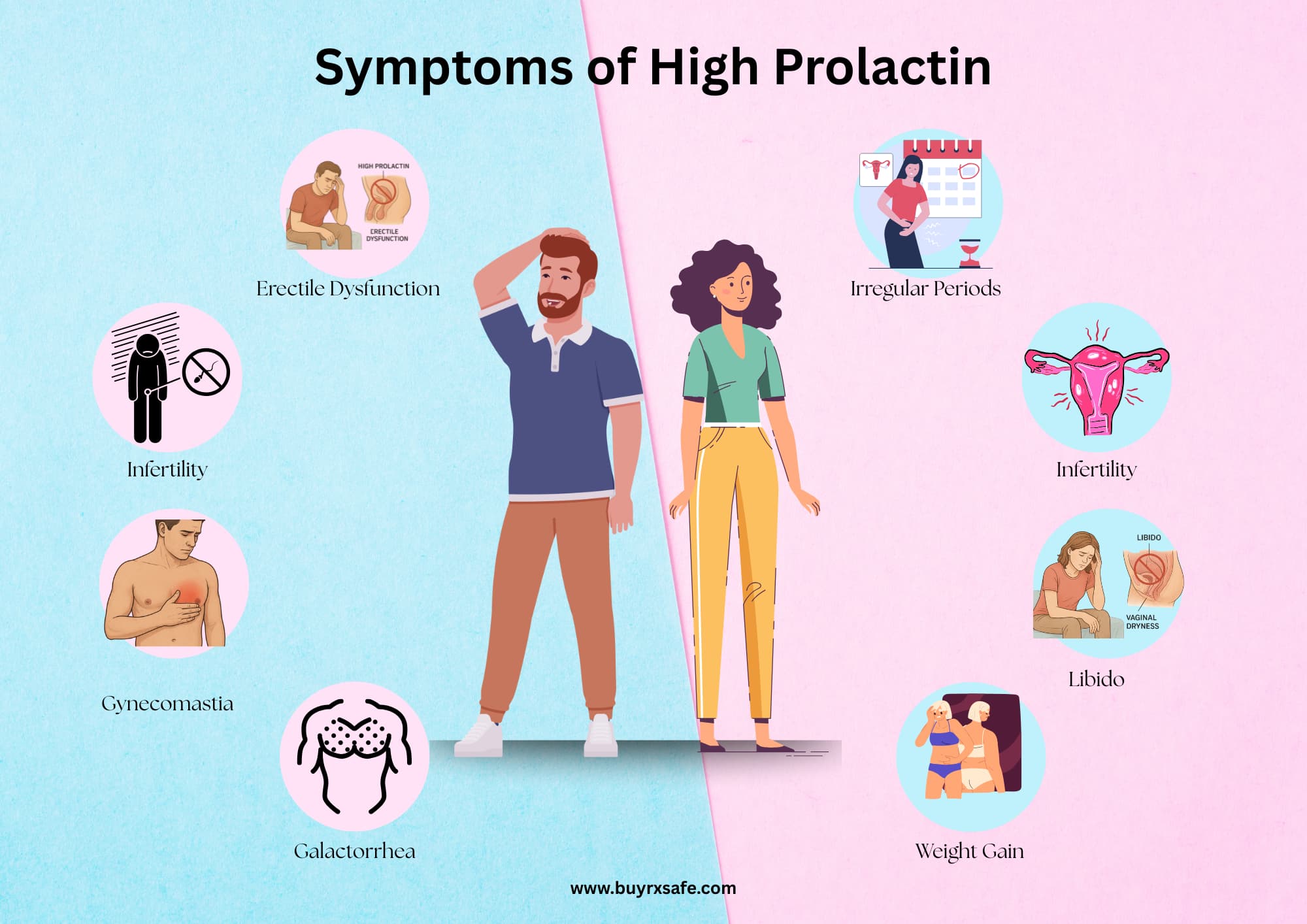
Recognising the Signs: Symptoms of High Prolactin
High Prolactin in Women:
It has a direct effect on your menstrual cycles, resulting in irregular or no periods at all (amenorrhea). This is the case, as an overabundance of prolactin inhibits ovulation hormones.
Due to the unexpected production of milk, also referred to as galactorrhea, you may notice this condition. This involves any discharge from any nipple that is not related to pregnancy or the delivery of a child; that is a big red flag.
It is known to cause infertility. High prolactin levels inhibit the ovulation of the egg, which makes conception hard because the hormones that trigger ovulation are not released.
It often causes a loss of sex drive (libido) and may cause vaginal drought. These are problems that are brought about by the related reduction of oestrogen levels.
You may get unexplained weight gain and perhaps acne. These are the symptoms that are associated with the general hormonal state of imbalance and low oestrogen caused by high prolactin.
Signs of High Prolactin in Males:
Hormonal imbalance and health-related problems of a man can be greatly impacted by high prolactin levels, which is called hyperprolactinemia. It is essential to be able to identify its symptoms to consult a doctor in time.
It often causes sexual dysfunction. High prolactin directly disrupts the testosterone production of the body, and this usually results in a pronounced loss of libido and erection problems (erectile dysfunction).
The ailment is a known cause of infertility in men. High prolactin may suppress (or completely prevent) the production of sperm (oligospermia), or simply cause the production to cease (azoospermia), making it difficult to conceive naturally.
It may result in unexpected changes to the breasts. High prolactin levels can stimulate breast tissue, leading to tenderness, swelling, or an apparent enlargement of the breast, known as gynecomastia. Although this is less common in men than in women.
In exceptional cases, it can cause galactorrhea. It is the secretion of a milky fluid that is sometimes oozed out of the breasts, which is definite and unusual and results in immediate medical attention.. It is the secretion of a milky fluid that is sometimes oozed out of the breasts, which is definite and unusual and results in immediate medical attention.
The Fertility Connection: Prolactin and Infertility
High levels of prolactin, a state referred to as hyperprolactinemia, are a well-known cause of infertility. The following is what you should know regarding the connection:

High prolactin has a direct effect of stopping pregnancy in that it suppresses the ovulation of the pituitary hormones and essentially stops your monthly cycle.
The natural conception with high prolactin has very little chance to happen because, in the absence of ovulation, one does not have an egg to fertilise the sperm.
Treatment mainly involves medication like cabergoline or bromocriptin, which is effective in reducing the levels of prolactin and returning normal ovulation.
Normal levels of prolactin must first be achieved by IVF treatment, as high levels may affect the implantation of embryos, which the doctor will control before commencing your ovarian stimulation.
An excellent prolactinoma will still allow you to have a safe pregnancy. The doctors will closely monitor you and usually recommend that you discontinue taking medication after your first trimester.
Although the connection between the two is not entirely evident, there is some indication that high prolactin levels can pose risks of miscarriage, and therefore, it is important to manage them before pregnancy.
What Causes High Prolactin? Pinpointing the Source
Pituitary Tumour / Pituitary Adenoma: The most common pathological cause.
High levels of prolactin, conditioned hyperprolactinemia, are most often a result of a benign pituitary tumour (prolactinoma). Such non-cancerous growths interfere with the normal functioning of the gland that ends up producing the hormone in excess.
The tumour size counts as a crucial factor. Microprolactinomas (less than 10mm) can have such symptoms as irregular periods or low libido. The larger macroprolactinomas may push against adjacent structures, causing headaches and vision problems by compressing the optic nerves.
Other factors may cause tumours in addition to tumours. Prolactin may be increased by common medications such as some antidepressants and antipsychotics. More so, there are also common malady conditions like hypothyroidism or chronic kidney disease, which are also culprits and need to be investigated.
Other Medical Conditions:
Hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid gland is a very typical medical reason behind a high proportion of prolactin. This is because the low thyroid hormone enhances the release of TRH hormone, which, in addition to stimulating prolactin release, also stimulates the release of growth hormone. Moreover, high prolactin levels may be caused by chronic kidney disease, as the kidneys are responsible for clearing the hormone from the blood. Other conditions like liver cirrhosis, particular seizure disorders, etc, can break this delicate hormonal balance.
Various popular drugs have been habitual offenders in increasing the level of prolactin. Some antipsychotics, antidepressants, and anti-nausea medications prevent dopamine in the brain directly. Because dopamine normally inhibits the secretion of prolactin, this inhibition permits prolactin to increase unregulated, which is referred to as medication-induced hyperprolactinemia.
The causes of high prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) are different. The typical causes are prescription drugs, underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), and chronic kidney disease. It may also be brought about by physical stressors such as trauma to the chest wall. In cases where a definite cause cannot be identified after a long period of searching, it is considered to be idiopathic hyperprolactinemia.
Getting a Diagnosis: The Path to Answers
To begin with, a simple blood test will make sure that your levels of prolactin are high.
After this, your doctor will request an MRI scan in order to see your pituitary gland well; this is a very important procedure that helps to eliminate or diagnose the presence of a benign tumour.
Then you should find an appointment with an endocrinologist, a specialist in hormones, who will then interpret these results and treat you.
This is a well-organised diagnostic procedure that gives concise responses and results in successful, individualised treatment.
Charting the Course: Prolactinoma Treatment Options
Prolactinoma is treated actively, and prolactin levels are brought down, which causes the tumour to shrink. This will be effective in relieving the symptoms such as headaches and visual changes, besides restoring normal sexual function and fertility. These are the goals normally achieved by doctors through dopamine agonist drugs.
Medication (First-Line Treatment):
The initial and most effective treatment of a prolactinoma is medication, i.e., cabergoline.
Cabergoline is preferred by physicians as it effectively reduces the levels of prolactin and the size of tumours as well, and most patients can comfortably use it.
On average, you should be prepared to take this medication at least two years before your specialist sees a possibility of a trial discontinuation.
Note that such adverse effects as nausea, dizziness, and fatigue can appear at first, but they are often temporary.
Bromocryptine is a good alternative form of treatment, even though it is not used so actively nowadays.
Prolactinoma Surgery (Transsphenoidal Surgery):
Surgery is required where the patients are unable to put up with the use of dopamine agonist drugs, where the tumour is resistant to the drugs, as well as sudden and severe vision loss caused by the tumour pressing against the optic nerves. It is also a choice for those who want a sure cure or in cases where the lady has a large prolactinoma and wants to have a child.
A minimally invasive method known as transsphenoidal surgery is the major procedure used by surgeons to reach the pituitary tumour via the nasal passage and has no external scar.
Tumour size and surgical expertise determine the high rates of success of this surgery. It is excessively high in the case of small tumours (microadenomas), which in most cases result in a cure, but much lower in the case of larger, invasive tumours (macroadenomas).
Natural Ways to Lower Prolactin & Prolactinoma Diet:
The following are supportive and natural measures to have in your medical treatment of a prolactinoma.
Make the process of managing stress a priority, and make sure you sleep properly and have enough sleep every night, as cortisol and sleep patterns may also play a role in the process of prolactin secretion.
Essential: Add a balanced, whole-foods diet that contains high amounts of antioxidants to maintain a healthy endocrine system.
There is some initial research that might indicate that there is a possible connection between Vitamin E and a decreased level of prolactin, although the available evidence is not conclusive yet.
Most importantly, never assume these lifestyle interventions as a substitute form of support to supplement your well-being in the strict adherence to the established medical care, as provided by your doctor.
Case Study Vignettes: A Global Perspective on Comorbidities
Treatment of chronic endocrine disorders such as prolactinoma, coupled with diabetes and weight problems, is an increasing international problem. The global healthcare systems are changing to accommodate such a complicated comorbidity and necessitate the need to apply combined care strategies to treat several related diseases together.
The healthcare systems in the world are now embracing integrated care models to treat hyperprolactinemia and other prevalent comorbidities, such as diabetes and weight problems.
Primary care providers and endocrinologists in the US and UK are actively involved in the coordination of care in patients who report multiple, interlinked hormone imbalances.
In countries such as Canada, Australia, and Scandinavia, priority is given to systematic lifestyle intervention programmes by the public health systems. The initiatives are directly related to the weight management objectives of patients who have high prolactin-related weight gain.
In France and Switzerland, research centres are at the forefront of the study of the more comprehensive metabolic implications of hormones to uncover further insight into these complicated interactions.
In the meantime, other nations like Thailand and Vietnam are turning to new interests in metabolic health management because the shift in diets is raising the occurrence of such diseases as prolactinoma.
This universal outlook highlights the fact that a holistic approach to treatment is urgent and must not focus on only one of the conditions of a patient.
Living and Thriving with Hyperprolactinemia
Follow your medication regimen as per the order; this is the basis of controlling prolactin levels and shrinking tumours.
Adhere to all planned follow-up MRI scans and blood tests, which would help to monitor your progress correctly and make any modifications to the treatment in time.
In case you want to be pregnant, make an initiative to visit a Fertility Specialist early on in your attempt to develop a personalised management strategy.
Take care of your entire body through healthy eating, physical exercise, and proper care in terms of stress management.
Conclusion
Do not overlook such signs as irregular periods, unexplained infertility, or low libido as stress and fatigue. These may be symptoms of hyperprolactinemia, which is a hormonal disorder that is treatable and in which the body may produce too much prolactin. Luckily, there is a distinct diagnosis trail to be followed, beginning with a straightforward blood test, to detect the underlying cause, which may run the gamut of medication side effects and a simple benign pituitary tumour. The trick is to find a professional examination, because these signs will have an extended effect on your health and well-being when you neglect them.
Having a proper diagnosis, there are very effective treatments that can be used to control your level of prolactin, reduce the symptoms, and effectively get you back to fertility. The most important thing that you can do to regain your health is to take action. We highly recommend this be followed with the help of an endocrinologist who would give you individualised recommendations and take you through a customised treatment regimen to meet your unique requirements.